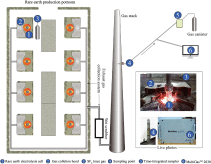
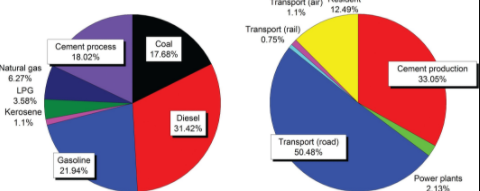
Inventory Compilation
-
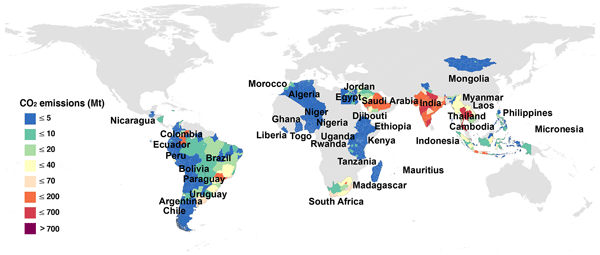
Energy-related CO2 emission accounts and datasets for 40 emerging economies in 2010–2019
Since 2000, CO2 emissions from emerging economies have outstripped those of developed economies. To limit global warming to under 1.5 ∘C by 2100, over 100 emerging economies have proposed net-zero carbon targets. Yet the supportive data are lacking – no inventory of CO2 emission outlines detailed sources by sector or distribution at the subnational level for these economies. Here, we redress the balance by establishing a dataset fo...
-
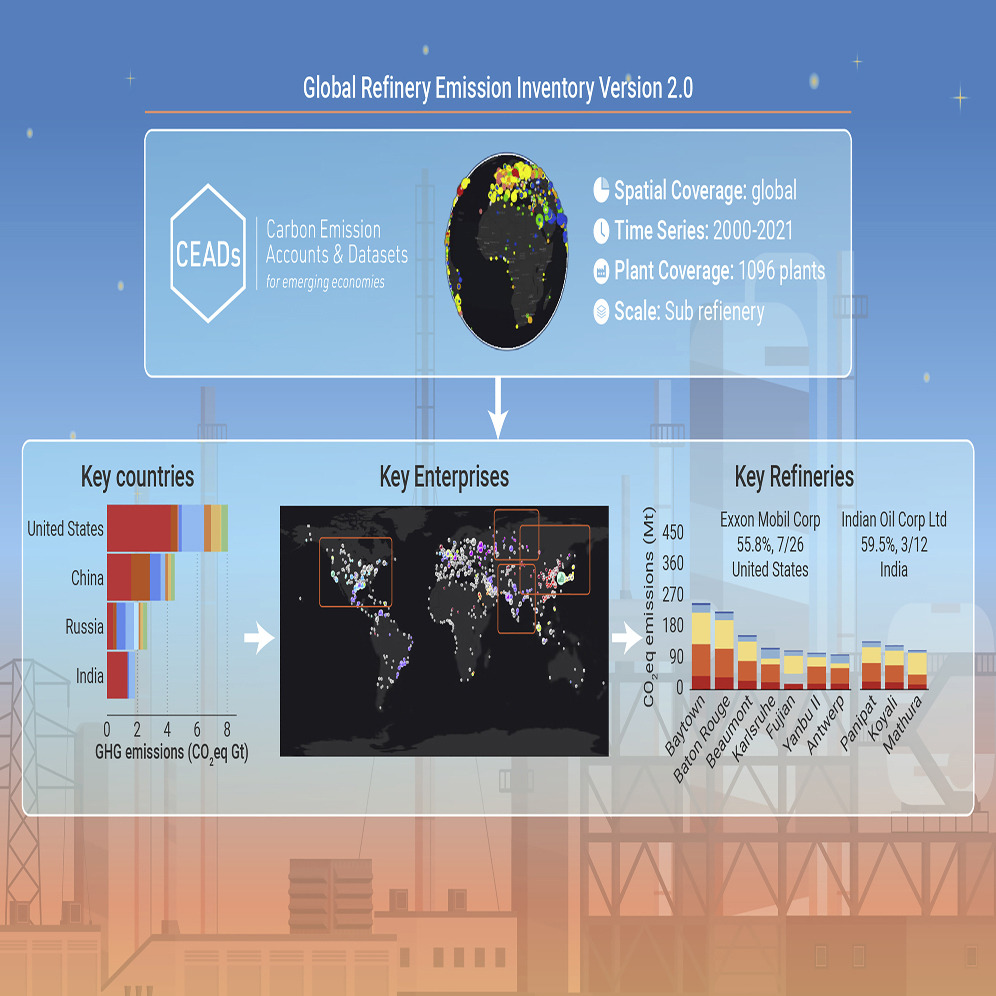
The contributions of key countries, enterprises and refineries to greenhouse gas emissions in global
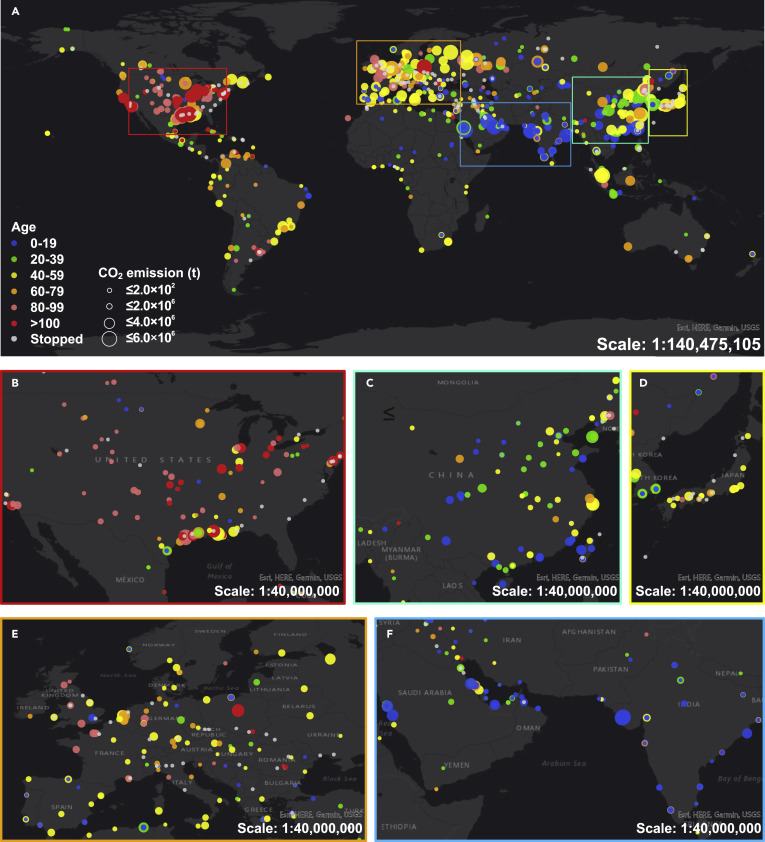
The refining industry is the third-largest source of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from stationary sources, so it is at the forefront of the energy transition and net zero pathways. The dynamics of contributors in this sector such as crucial countries, leading enterprises, and key emission processes are vital to identifying key GHG emitters and supporting targeted emission reduction, yet they are still poorly understood. Here, we...
-
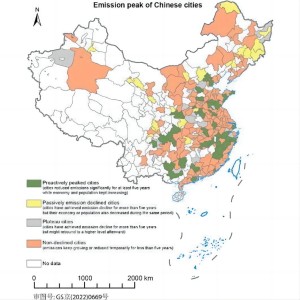
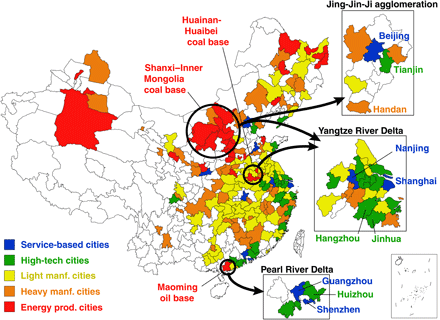
City-level emission peak and drivers in China
China is playing an increasing role in global climate change mitigation, and local authorities need more city-specific information on the emissions trends and patterns when designing low-carbon policies. This study provides the most comprehensive CO2 emission inventories of 287 Chinese cities from 2001 to 2019. The emission inventories are compiled for 47 economic sectors and include energy-related emissions for 17 types of fossil fuels ...
-
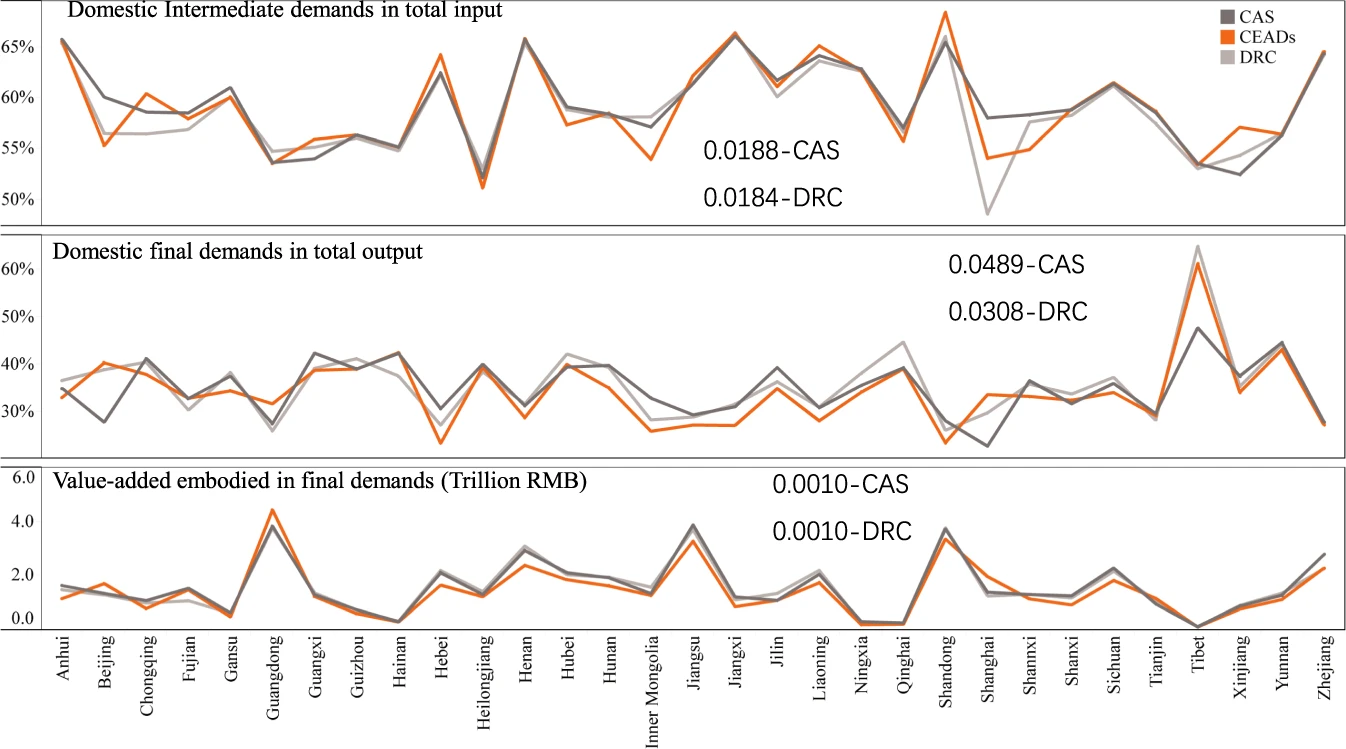
Chinese provincial multi-regional input-output database for 2012, 2015, and 2017
Global production fragmentation generates indirect socioeconomic and environmental impacts throughout its expanded supply chains. The multi-regional input-output model (MRIO) is a tool commonly used to trace the supply chain and understand spillover effects across regions, but often cannot be applied due to data unavailability, especially at the sub-national level. Here, we present MRIO tables for 2012, 2015, and 2017 for 31 provinces of...
-
Adaptive CO2 emissions mitigation strategies of global oil refineries in all age groups
Continuous expansion of fossil fuel-based energy infrastructure can be one of the key obstacles in delivering the Paris Agreement goals. The oil refinery is the world's third-largest stationary emitter of greenhouse gases (GHGs), but the historical mapping of the regional-specific refining industry, their CO2 emission patterns, and mitigation potentials remain understudied. This study develops a plant-level, technical-specific, and time-...
-
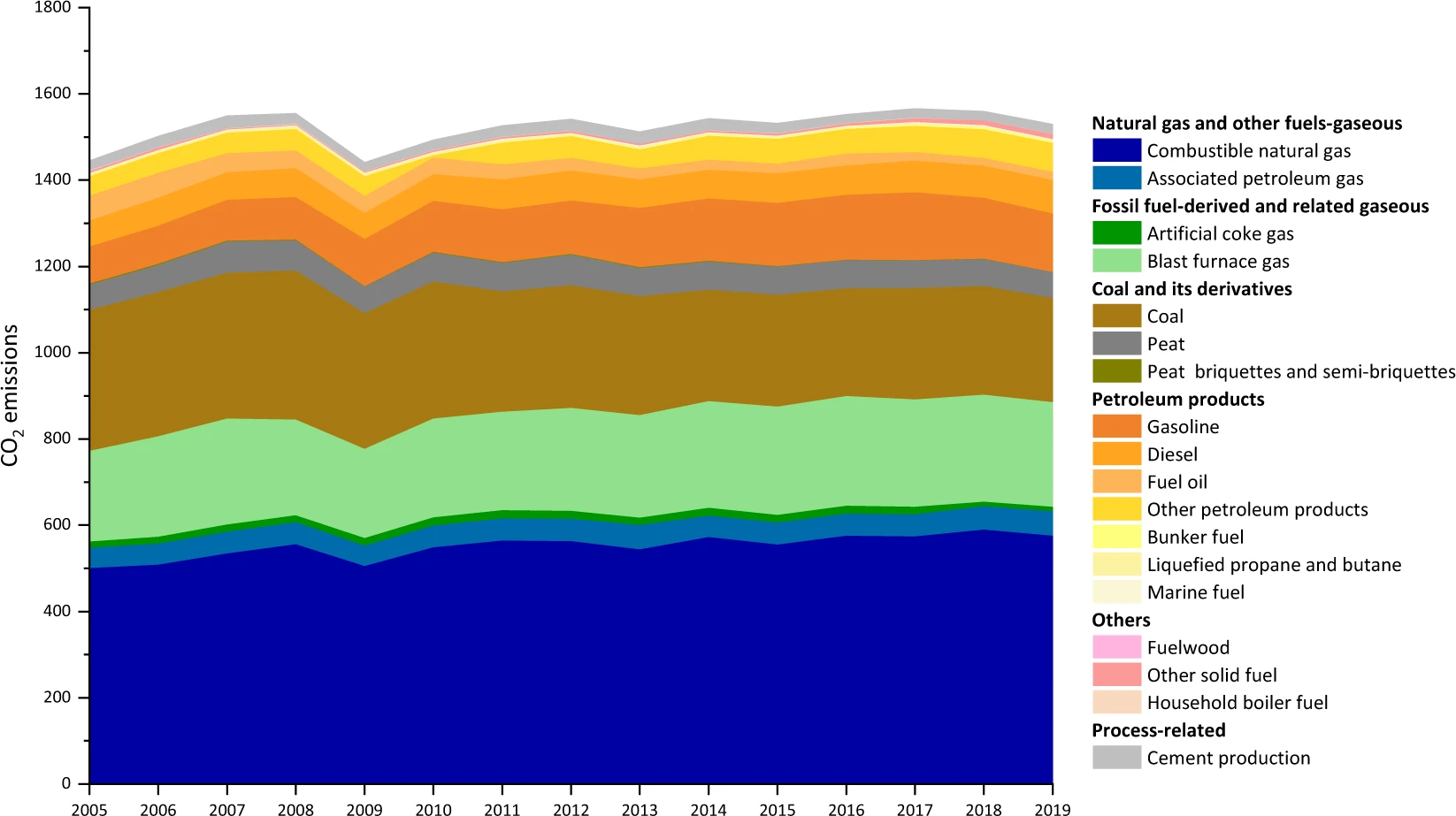
CO2 emission accounts of Russia’s constituent entities 2005–2019
Constituent entities which make up Russia have wide-ranging powers and are considered as important policymakers and implementers of climate change mitigation. Formulation of CO2 emission inventories for Russia’s constituent entities is the priority step in achieving emission reduction. Russia is the world’s largest exporter of oil and gas combined and the fourth biggest CO2 emitter, so it’s efforts in mitigating CO2 emissions are g...
-
Japan prefectural emission accounts and socioeconomic data 2007 to 2015
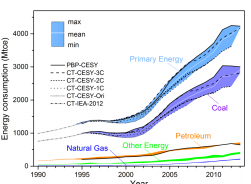
In the wake of the Fukushima nuclear disaster, Japanlargely moved away from nuclear power generation and turned back towards anenergy sector dominated by fossil fuels. As a result, the pace towards reachingemission reduction targets has largely slowed down. This situation indicatesthat higher emissions will continue to be generated if there is no appropriateand efficient measurement implemented to bridge the energy demand gap. Tocontribu...
-
Low-carbon development via greening global value chains: a case study of Belarus
The rise of global value chains (GCVs) hasseen the transfer of carbon emissions embodied in every step of internationaltrade. Building a coordinated, inclusive and green GCV can be an effective andefficient way to achieve carbon emissions mitigation targets for countries thatparticipate highly in GCVs. In this paper, we first describe the energyconsumption as well as the territorial and consumption-based carbon emissionsof Belarus and i...
-
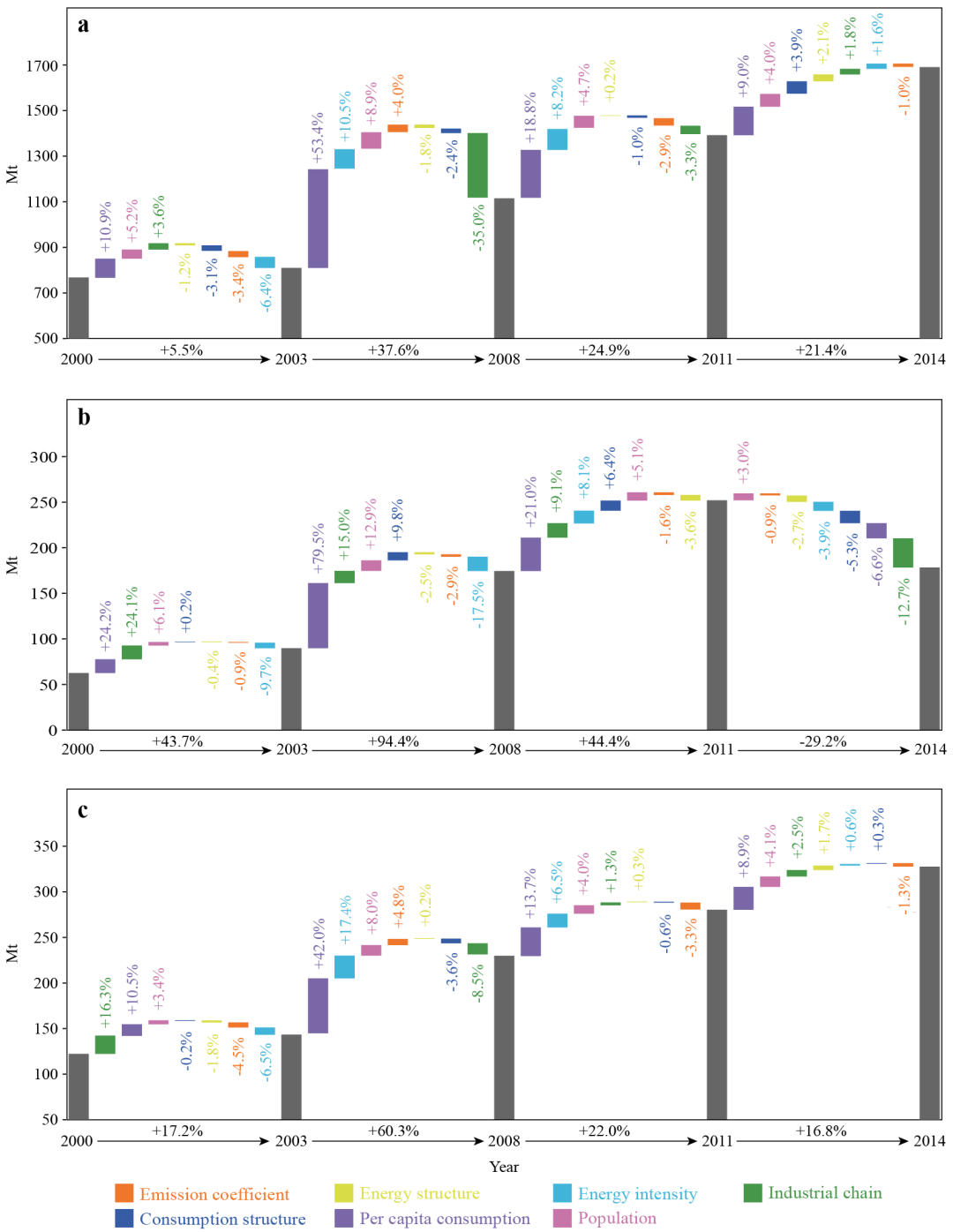
Dynamic Driving Forces of India's Emissions from Production and Consumption Perspectives
While India becomes one of the largest carbon emittersin the world with a high emission growth rate, existing studies fail to capturethe recent trends and the key driving factors behind it. Here, by usingmultiregional input-output analysis and structural decomposition analysis, wemeasure the contribution of factors to the changes of India's domesticconsumption and trade-related emissions. This study finds that India's percapita consumpti...
-
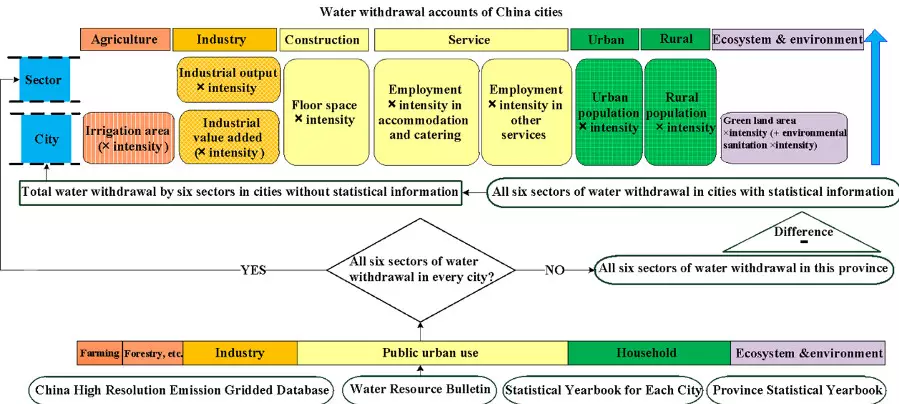
City-level Water Withdrawal in China: Accounting Methodology and Applications
In the context of the freshwater crisis,accounting for water withdrawal could help planners better regulate water usein different sectors to combat water scarcity. However, the water withdrawalstatistics in China are patchy, and the water data across all sectors at thecity level appear to be relatively insufficient. Hence, we develop a generalframework to, for the first time, estimate the water withdrawal of 58economic-social-environmen...
-
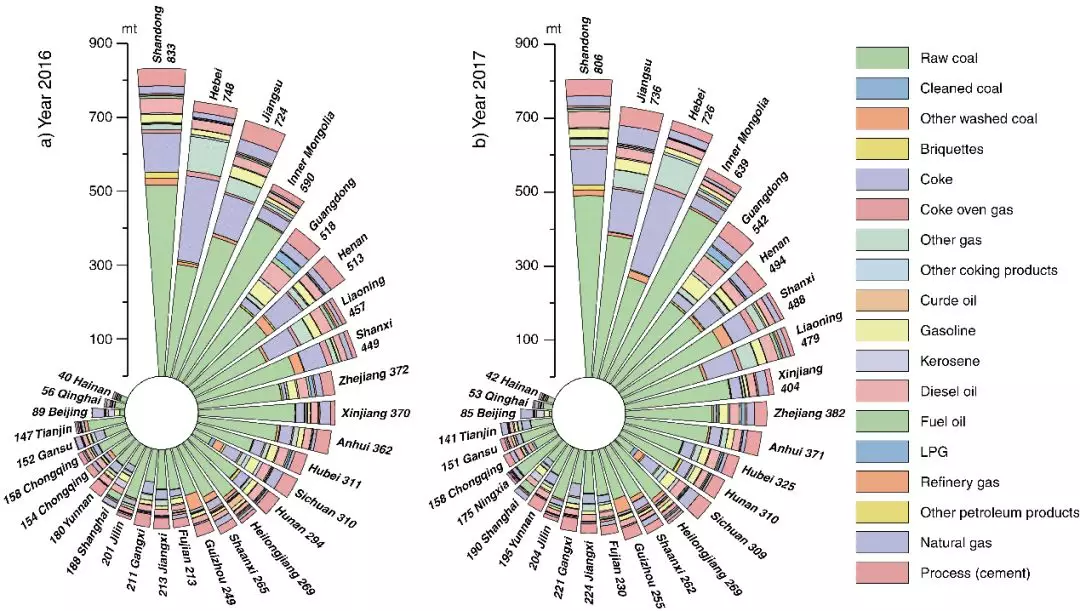
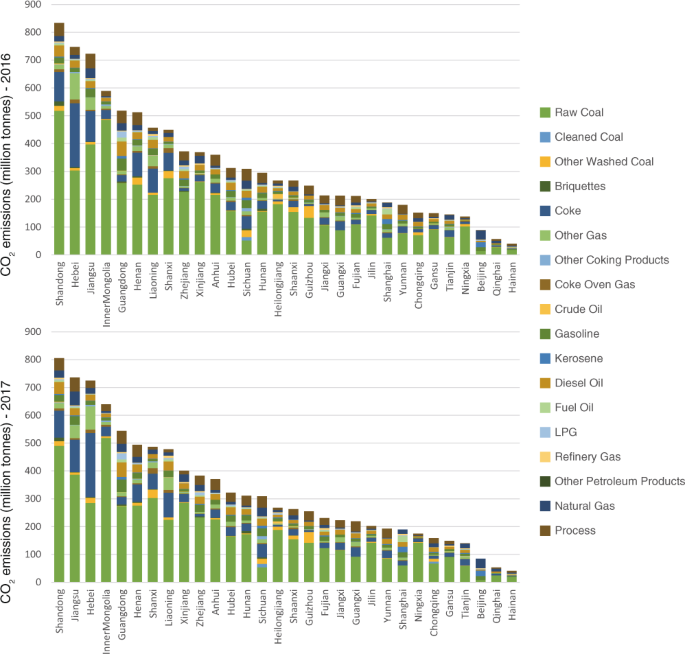
China CO2 emission accounts 2016-2017
Despite China’s emissions having plateaued in 2013, itis still the world’s leading energy consumer and CO2 emitter, accounting forapproximately 30% of global emissions. Detailed CO2 emission inventories byenergy and sector have great significance to China’s carbon policies as well asto achieving global climate change mitigation targets. This study constructsthe most up-to-date CO2 emission inventories for China and its 30 provinces...
-
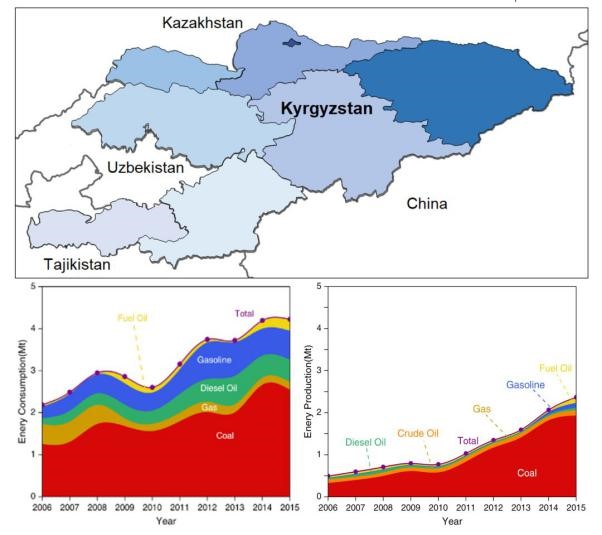
Carbon emissions in countries that failed to ratify the intended nationally determined contributions
The Paris Agreement aims to increase globalparticipation in climate change actions, yet attentions are not equally givenamong countries. The knowledge gap remains in understanding the structure anddrivers of the emission in small developing countries. Eighteen countries havefailed to ratify their Intended National Determined Contributions (INDCs) as anofficially recognized emission target. Among these countries, we choseKyrgyzstan as a ...
-
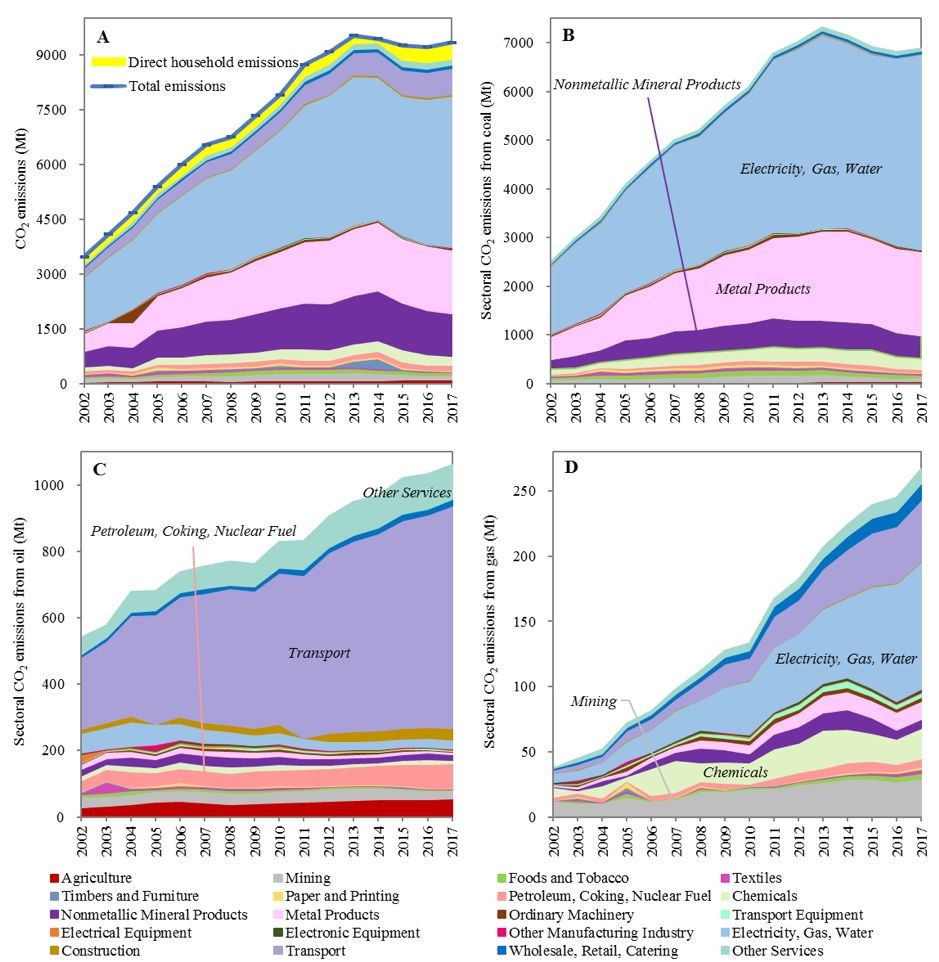
The slowdown in China’s carbon emissions growth in the new phase of economic development
China’s CO2 emissions have plateaued underits commitment to reaching peak carbon emissions before 2030 in order tomitigate global climate change. This commitment is aligned with China’s turn toward more sustainabledevelopment, named“the new normal”phase. This study aims to explore the role of possiblesocioeconomic drivers of China’s CO2 emission changes by using structural decomposition analysis(SDA) for 2002-2017. The results...
-
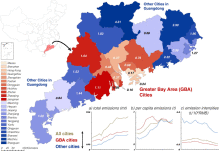
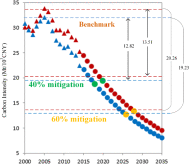
Emissions and low-carbon development in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area cities and their
Cities are the major contributors to energy consumption and CO 2 emissions, as well as being leading innovators and implementers of policy measures in climate change mitigation. Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) is an agglomeration of cities put forward by China to strengthen international cooperation among “Belt and Road” countries and promote low-carbon, inclusive, coordinated and sustainable development. Few studies...
-
Distinguishing Emission-Associated Ambient Air PM2.5 Concentrations and Meteorological Factor-Induce
Although PM 2.5 (particulate matter with aerodynamic diameters less than 2.5 μm) in the air originates from emissions, its concentrations are often affected by confounding meteorological effects. Therefore, direct comparisons of PM 2.5 concentrations made across two periods, which are commonly used by environmental protection administrations to measure the effectiveness of mitigation efforts, can be misleading. Here, we developed a two-...
-
How modifications of China's energy data affect carbon mitigation targets
Frequent modifications to energy statistics have led to considerable uncertainty in China's ability to achieve its carbon mitigation targets. Here, we quantitatively measure the impact of energy data revisions on China's ability to achieve its mitigation targets. Our results indicate the following effects of data revisions: 1. Mitigation challenges have increased by 5%, and the achievement of national mitigation targets (as well as inter...
-
Decreases in global beer supply due to extreme drought and heat
Beer is the most popular alcoholic beverage in the world by volume consumed, and yields of its main ingredient, barley, decline sharply in periods of extreme drought and heat. Although the frequency and severity of drought and heat extremes increase substantially in range of future climate scenarios by five Earth System Models, the vulnerability of beer supply to such extremes has never been assessed. We couple a process-based crop model...
-
Assessment of the economic impacts of heat waves: A case study of Nanjing, China
The southeast region of China is frequently affected by summer heat waves. Nanjing, a metropolitan city in Jiangsu Province, China, experienced an extreme 14-day heat wave in 2013. Extreme heat can not only induce health outcomes in terms of excess mortality and morbidity (hospital admissions) but can also cause productivity losses for self-paced indoor workers and capacity losses for outdoor workers due to occupational safety requireme...
-
Assessment of the pollution–health–economics nexus in China
Serious haze can cause contaminant diseases that trigger productive labour time by raising mortality and morbidity rates in cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. Health studies rarely consider macroeconomic impacts of industrial interlinkages while disaster studies seldom involve air pollution and its health consequences. This study adopts a supply-driven input–output model to estimate the economic loss resulted from disease-induced...
-
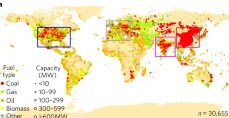
Targeted emission reductions from global super-polluting power plant units
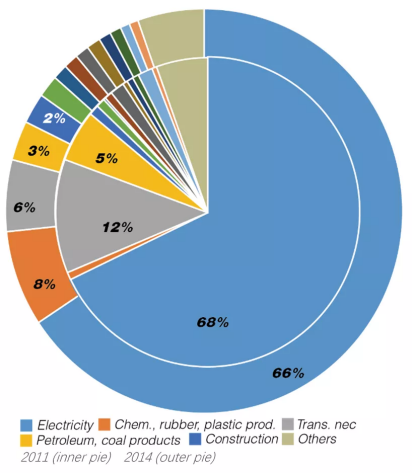
There are more than 30,000 biomass- and fossil-fuel-burning power plants now operating worldwide, reflecting a tremendously diverse infrastructure, which ranges in capacity from less than a megawatt to more than a gigawatt. In 2010, 68.7% of electricity generated globally came from these power plants, compared with 64.2% in 1990. Although the electricity generated by this infrastructure is vital to economic activity worldwide, it also pr...
-
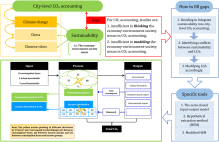
Integrating Sustainability Into City-level CO2 Accounting: Social Consumption Pattern and Income Dis
From a sustainability perspective, city-level CO 2 emissions require reconsiderations. Correspondingly, the economy-environment-society nexus should be incorporated into city-scale CO 2 accounting. Therefore, in this study, the semi-closed IO model is integrated with a HEM to calculate CO 2 emissions arising from the social consumption pattern and income distribution, and to explore economic drivers behind CO 2 variations. This method i...
-
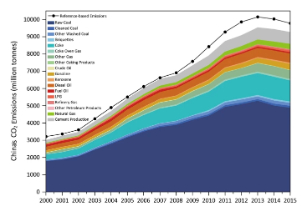
China CO2 emission accounts 1997–2015
China is the world’s top energy consumer and CO 2 emitter, accounting for 30% of global emissions. Compiling an accurate accounting of China’s CO 2 emissions is the first step in implementing reduction policies. However, no annual, officially published emissions data exist for China. The current emissions estimated by academic institutes and scholars exhibit great discrepancies. The gap between the different emissions estimates is ap...
-
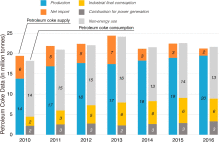
Rapid growth of petroleum coke consumption and its related emissions in China
Petroleum coke, a non-environmentally friendly energy source, is gradually replacing other power fuels in China’s industrial enterprises because of its price advantage. Petroleum coke has high emission factors and thus emits more greenhouse gases (GHGs) and air pollutants than even raw coal. This study first examines the rapid growth of petroleum coke consumption in China since 2010 by industry sector and region and then estimates the ...
-
City-level climate change mitigation in China
As national efforts to reduce CO 2 emissions intensify, policy-makers need increasingly specific, subnational information about the sources of CO 2 and the potential reductions and economic implications of different possible policies. This is particularly true in China, a large and economically diverse country that has rapidly industrialized and urbanized and that has pledged under the Paris Agreement that its emissions will peak by 2030...
-
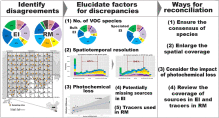
Reconciling discrepancies in the source characterization of VOCs between emission inventories and re
Emission inventory (EI) and receptor model (RM) are two of the three source apportionment (SA) methods recommended by Ministry of Environment of China and used widely to provide independent views on emission source identifications. How to interpret the mixed results they provide, however, were less studied. In this study, a cross-validation study was conducted in one of China's fast-developing and highly populated city cluster- the Pearl...
-
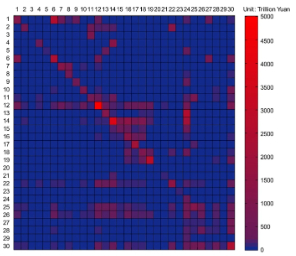
A multi-regional input-output table mapping China's economic outputs and interdependencies in 2012
Multi-regional input-output (MRIO) models are one of the most widely used approaches to analyse the economic interdependence between different regions. We utilised the latest socioeconomic datasets to compile a Chinese MRIO table for 2012 based on the modified gravity model. The MRIO table provides inter-regional and inter-sectoral economic flows among 30 economic sectors in China’s 30 regions for 2012. This is the first MRIO table to ...
-
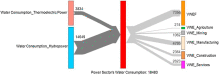
Categorising virtual water transfers through China’s electric power sector
Water consumption in thermoelectric and hydropower plants in China increased from 1.6 and 6.1 billion m 3 , respectively, to 3.8 and 14.6 billion m 3 from 2002 to 2010. Using the concept of virtual water, we attribute to different electricity users the total water consumption by the electric power sector. From 2002 to 2010, virtual water embodied in the final consumption of electricity (hereinafter referred to as VWEF) increased from 1.9...
-
Estimating perfluorocarbon emission factors for industrial rare earth metal electrolysis
Rare earth (RE) metals have been widely applied in new materials, leading to their drastic production increase in the last three decades. In the production process featured by the molten-fluoride electrolysis technology, perfluorocarbon (PFC) emissions are significant and therefore deserve full accounting in greenhouse gas (GHG) emission inventories. Yet, in the ‘ 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories ’, no met...
-
Local strategies for China's carbon mitigation: An investigation of Chinese city-level CO2 emissions
This paper provides a systematic analysis that identifies the driving forces of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions of 286 Chinese prefecture-level cities in 2012. The regression analysis confirms the economic scale and structure effects on cities' CO 2 emissions in China. If China's annual economic growth continues at the rate of 7%, CO 2 emissions will increase by about 6% annually. In addition, climate conditions, urbanization and public...
-
Energy consumption and CO2 emissions in Tibet and its cities in 2014: Tibet CO2 emissions in 2014
Because of its low level of energy consumption and the small scale of its industrial development, the Tibet Autonomous Region has historically been excluded from China’s reported energy statistics, including those regarding CO2 emissions. In this paper, we estimate Tibet’s energy consumption using limited online documents, and we calculate the 2014 energy-related and process-related CO2 emissions of Tibet and its seven prefecture-lev...
-
Methodology and applications of city level CO2 emission accounts in China
China is the world's largest energy consumer and CO 2 emitter . Cities contribute 85% of the total CO 2 emissions in China and thus are considered as the key areas for implementing policies designed for climate change adaption and CO 2 emission mitigation. However, the emission inventory construction of Chinese cities has not been well researched, mainly owing to the lack of systematic statistics and poor data quality. Focusing on this r...
-
Variations of China's emission estimates: Response to uncertainties in energy statistics
The accuracy of China's energy statistics is of great concern because it contributes greatly to the uncertainties in estimates of global emissions. This study attempts to improve the understanding of uncertainties in China's energy statistics and evaluate their impacts on China's emissions during the period of 1990–2013. We employed the Multi-resolution Emission Inventory for China (MEIC) model to calculate China's emissions based on d...
-
Assessment of socioeconomic costs to China’s air pollution
Particulate air pollution has had a significant impact on human health in China and it is associated with cardiovascular and respiratory diseases and high mortality and morbidity. These health impacts could be translated to reduced labor availability and time. This paper utilized a supply-driven input-output (I-O) model to estimate the monetary value of total output losses resulting from reduced working time caused by diseases related to...
-
Accounting for value added embodied in trade and consumption: an intercomparison of global multiregi
Global multiregional input–output (MRIO) tables constitute detailed accounts of the economic activity worldwide. Global trade models based on MRIO tables are being used to calculate important economic and environmental indicators such as value added in trade or the carbon footprint of nations. Such applications are highly relevant in international trade and climate policy negotiations, and consequently MRIO model results are being scru...
-
Carbon emissions from fossil fuel consumption of Beijing in 2012
The present study analyzed the consumption-based carbon emissions from fossil fuel consumption of Beijing in 2012. The multi-scale input–output analysis method was applied. It is capable of tracing the carbon emissions embodied in imports based on a global multi-regional input–output analysis using Eora data. The results show that the consumption-based carbon emission of Beijing has increased by 18% since 2007, which is 2.57 times hi...
-
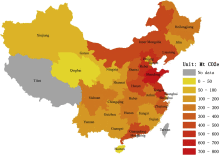
New provincial CO2 emission inventories in China based on apparent energy consumption data and updat
This study employs “apparent energy consumption” approach and updated emissions factors to re-calculate Chinese provincial CO 2 emissions during 2000–2012 to reduce the uncertainty in Chinese CO 2 emission estimates for the first time. The study presents the changing emission-socioeconomic features of each provinces as well. The results indicate that Chinese provincial aggregated CO 2 emissions calculated by the apparent energy con...
-
Income-Based Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Nations
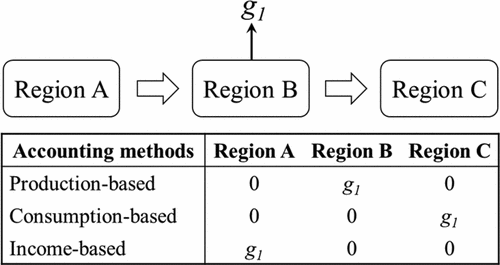
Accounting for greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of nations is essential to understanding their importance to global climate change and help inform the policymaking on global GHG mitigation. Previous studies have made efforts to evaluate direct GHG emissions of nations (a.k.a. production-based accounting method) and GHG emissions caused by the final consumption of nations (a.k.a. consumption-based accounting method), but overlooked downstre...
-
Reduced carbon emission estimates from fossil fuel combustion and cement production in China
Nearly three-quarters of the growth in global carbon emissions from the burning of fossil fuels and cement production between 2010 and 2012 occurred in China 1 , 2 . Yet estimates of Chinese emissions remain subject to large uncertainty; inventories of China’s total fossil fuel carbon emissions in 2008 differ by 0.3 gigatonnes of carbon, or 15 per cent 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 . The primary sources of this uncertainty are conflicting estimates of...
-
Assessment of China's virtual air pollution transport embodied in trade by using a consumption-based
Substantial anthropogenic emissions from China have resulted in serious air pollution, and this has generated considerable academic and public concern. The physical transport of air pollutants in the atmosphere has been extensively investigated; however, understanding the mechanisms how the pollutant was transferred through economic and trade activities remains a challenge. For the first time, we quantified and tracked China's air pollut...
-
CO2 emissions from China’s lime industry
China is now the world’s leading energy consumer and CO 2 emitter; therefore, precise quantification of the CO 2 emissions that occur in China is of serious concern. Although most studies focus on CO 2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion and cement production, the emissions from lime production is not well researched. Lime production is the second largest source of carbon emissions from industrial processes after cement production. T...
-
Four system boundaries for carbon accounts
Knowing the carbon emission baseline of a region is a precondition for any mitigation effort, but the baselines are highly dependent on the system boundaries for which they are calculated. On the basis of sectoral energy statistics and a nested provincial and global multi-regional input–output model, we calculate and compare four different system boundaries for China's 30 provinces and major cities. The results demonstrate significant ...
-
CO2 emissions from China’s power sector at the provincial level: Consumption versus production per
The Chinese electricity sector plays an important role in domestic CO 2 mitigation efforts due to its large contribution to overall emissions. However, primary energy resources used for electricity generation are not evenly distributed across the country. Such a supply and demand mismatch in reality results in large parts of electricity to be transferred from economically less developed provinces in the west to economic growth centres in...
-
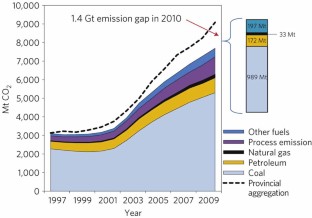
The gigatonne gap in China’s carbon dioxide inventories
Reliable national statistics are fundamental for climate change science as well as for global negotiations about future emission targets and the allocation of responsibilities. China, the world’s top CO 2 emitter 1 , 2 , has frequently been questioned about its data transparency and accuracy of energy and emission statistics 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 . China implemented a top-down statistical system where energy statistics are compiled under t...
-
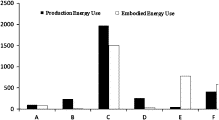
Embodied energy use in China's industrial sectors
As the world’s top energy consumer, China is facing a great challenge to solve its energy supply issue. In this paper energy use from all industrial sectors in China’s economy of 2007 was explored by conducting an extended environmental input–output analysis . We compare the energy consumption embodied in the final demand for goods and services from 29 sectors with the energy demand required for the actual production process in eac...
-
Uncovering China’s greenhouse gas emission from regional and sectoral perspectives
Understanding China’s GHG (greenhouse gas) emission status is critical for achieving the national mitigation plan. While much attention has addressed China’s national level GHG emission, less is known about its regional and sectoral emission features. In this paper China’s regional and sectoral GHG emission patterns and their driving forces were explored by using upgraded energy consumption data. We constructed a detailed GHG inven...